Array:-
An array is an index collection of fixed number of homogeneous data elements.
The main advantage of an array is we can represent a huge number of elements by a single variable.
But the main disadvantage of an array is it is fixed in size so that once the array is created then there is no chance of increasing the size of the array based on our requirement.
Hence to use an array, we should know the size in advance.
Array Declaration;-
How to declare an array?
Let's see in how many ways we can declare an array.
1-D Array Declaration:-
int [ ] x; (Recommended to use)
int [ ]x;
int x[ ];
Above all three declaration of the 1-D array is valid.If we are using other than this then we will get compile time error.
2-D Array Declaration:-
int [ ][ ] x;
int [ ][ ]x;
int x[ ][ ];
int [ ] x [ ];
int [ ] [ ]x;
int [ ]x [ ];
Above all declaration of 2-D array is valid.If we are using other than this than we will get compile time error.
3-D Array Declaration:-
int [ ][ ][ ] x;
int [ ][ ][ ] x;
int x[ ][ ][ ] ;
int [ ] x[ ][ ] ;
int [ ] [ ][ ]x;
int [ ] [ ] x[ ] ;
int [ ][ ] [ ]x;
int [ ][ ] x[ ];
int [ ][ ]x[ ];
int [ ]x [ ][ ];
Above all declaration of 3-D array is valid. If we are using other than this than we will get compile time error.
Array Creation In JAVA
How to Create an Array:-
Every Array in java is an object.
Hence we can create an array by using new operator or keyword.
example:-
int [ ] a=new int [3] ;
Rules For Creating an Array:-
1.At the time of Array creation compulsory, we should specify the size otherwise, we will get compile time error.
example:-
int [ ] x= new [ ]; (invalid)
int [ ] x= new [ 6 ]; (valid)
2.It is legal to have an Array with size 0 in java.
example:-
int [ ] x= new [ 0 ]; (valid)
3.If we are trying to specify array size with negative int value then we will get RunTime Exception saying
" NegativeArraySizeException".
example:-
int [ ] x= new [-3 ]; (invalid)
RuntimeException:- " NegativeArraySizeException".
But we won't get any Compile Time Error.The code will compile fine.
4.To specify Array size allowed data types are the byte, short, char, int.
If we are trying to specify any other than that then we will get compile time array.
example:-
int [ ] x= new [ 10]; (valid)
int [ ] x= new [ 'a']; (valid)
byte c=20
int [ ] x= new [ c]; (valid)
short s=30;
int [ ] x= new [ s]; (valid)
int [ ] x= new [ 10 L]; (invalid)
Compile Time Error:- Possible loss of precision
found: -long
required: -int
5.The maximum Array size in java is 2147483647 which is nothing but the maximum value of int data type.
int [ ] x= new [ 2147483647]; (valid)
int [ ] x= new [ 2147483648]; (invalid)
Compile Time Error: Integer Number Too Large
Note: In the 1st example of rule 5 we may get Runtime Exception if sufficient heap memory is not available.
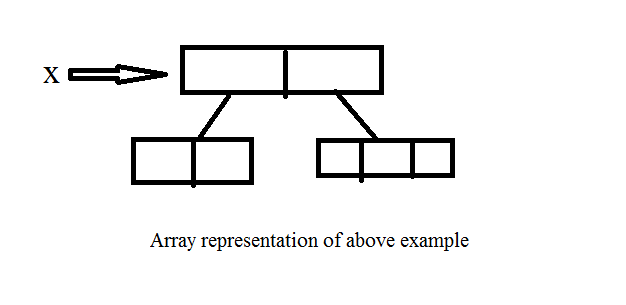
2-D Array
To create a 2-D array or multidimensional Array we have to specify the base size of the Array.Because we are using new operator for allocating memory to an array so Compulsory we should provide size at least base.For Array, creation java follows Array of Array Approach.
example 1:
If we are not Specifying the base size then we will get Compile time Error.
x[ 0] =new int [2];
x[1] =new int [3];
Memory representation of above example:
 example 2:
example 2:int [ ] [ ][ ] x =new int [ 3] [ ] [ ]; (valid)
In the above example, we provided the base value 3. Rest of we kept empty which is valid in java.
we won't get any compile time error or runtime exception;
example 3:
int [ ] [ ] x = new int [ ] [ 2]; (invalid)
In the above example we did' provide any base value,means base index is empty so it is wrong in java.
Hence we will get Compile time Error.
Que:
which of Array Declaration are valid?
int [ ] a =new int [ ];
int [ ] a =new int [ 3];
int [ ] [ ] a =new int [ ] [ ];
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ ];
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ ] [ 4];
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [3 ];
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ 4] [ 5];
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ ] [ 1] [2 ];
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ ] [3 ];
Now scroll down for check your answers;
Ans
int [ ] a =new int [ ]; (invalid)
int [ ] a =new int [ 3]; (valid)
int [ ] [ ] a =new int [ ] [ ]; (invalid)
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ ]; (valid)
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ ] [ 4]; (invalid)
int [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [3 ]; (valid)
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ 4] [ 5]; (valid)
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ 4] [ 3]; (valid)
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ ] [ 1] [2 ]; (invalid)
int [ ] [ ] [ ]a =new int [ 2] [ ] [3 ]; (valid)
Array Initialization:-
Once we create an array every element by default initialize by default values.
example 1:
int [ ] x =new int [ 3];
System.out.println(x[0]); o/p is 0 (default initial value)
System.out.println(x[1]); o/p is 0 (default initial value)
System.out.println(x[2]); o/p is 0 (default initial value)
System.out.println(x); o/p is [ I@3e25a5
surprise What is this number???
Remember Carefully that whenever we are trying to print any reference variable internally toString()
the method will be called which is by default implemented to return in the following from.
Classname@hashcode_in_hexadecimalform
means
[ is 1-D array
I is for Integer class
@3e25a5 hashcode (For every system it is different)
List of corresponding classes:
example 2:
int [ ] [ ] x = new int [3] [ 2]
System.out.println(x); o/p is [ [ I@3e15a9
System.out.println(x[0]); o/p is [ I@5e25a5
System.out.println(x[0][0]); o/p is 0 (default initial value)
let take a look at the memory representation:-
example 3:
int [ ] [ ] x= new int [ 3] [ ];
System.out.println(x); o/p is [ [ I@3e15a9
System.out.println(x[0]); o/p is null
System.out.println(x[0][0]); no o/p we will get "NullPointerException"
because we are trying to operate on null.
Once we creates an array every array element by default initialize values ,if we are not satisfied with default values then we can override these values with our customized values.
for example:
int [ ] x= new int [3];
x[0]=40;
x[1]=50;
x[2]=60;
System.out.println(x[0]) o/p is 40;
System.out.println(x[1]) o/p is 50;
System.out.println(x[2]) o/p is 60;
Shortcut method for Array Declaration,Creation,Initialization into a single line
1.For 1-D Array:-
We can declare, create & initialize an array into a single line.
This is the short cut method what we are discussing here.
let's go...
example :
int [ ] x= new int [3];
x[0]=10;
x[1]=20;
x[2]=30;
we can do this into a single line as follows:-
int [ ] x={10,20,30}; (perfectly valid)
But if we want to use this shortcut compulsory we should perform all activities into a single line only.
if we are trying to do in multiple lines then we will get Compile-Time Error.
example:-
int [ ] x ; Declaration is valid
x={10,20,30} But Compile-Time Error : Illegal start of Expression
2.For 2-D Array:-
we can use this shortcut method even for multidimensional array also.
int [ ] [ ] x={{10,20},{30,40,50}}; (perfectly valid)
3. For 3-D Array
example:
int [ ] [ ] [ ] x = int {{{10,20,30},{40,50,60}},{{70,80},{90,100,110}}};
Try to find out the outputs:-
System.out.println(x[0][1][2]);
System.out.println(x[1][0][1]);
System.out.println(x[2][0][0]);
System.out.println(x[1][2][0]);
System.out.println(x[1][1][1]);
Now scroll down for answers:
System.out.println(x[0][1][2]); o/p is 60
System.out.println(x[1][0][1]); o/p is 80
System.out.println(x[2][0][0]); Runtime Exception :ArrayIndesxBoundException
System.out.println(x[1][2][0]); Runtime Exception :ArrayIndesxBoundException
System.out.println(x[1][1][1]); o/p is 100
How to find length of an Array
We can find the length of an array by using length variable.
1. length variable:-
length is a final variable applicable for arrays.
length variable represents the size of an array.
example:
int [ ] x = new int [6];
System.out.println(x.length); o/p is 6 .
int [ ] x =new int [10;
System.out.println(x.length); o/p is 10 .
System.out.println(x.length());
Compile-Time Error: cannot find symbol
Symbol: method length()
location: class int [ ]
But Do not Apply length( ) method here.Because length( ) is applicable for String.
2.length ( ) method:-
length( ) is a final method appicable for String Objects/
length( ) return the numbers of character present in the String.
example:
String s="javabychetan";
System.out.println(s.length()); o/p is 12
System.out.println(s.length);
Compile-Time Error: cannot find symbol
Symbol: variable length
location: class java.lang.String









No comments:
Post a Comment
Be the first to comment!
Don't just read and walk away, Your Feedback Is Always Appreciated. I will try to reply to your queries as soon as time allows.
Note:
1. If your question is unrelated to this article, please use our Facebook Page.
2. Please always make use of your name in the comment box instead of anonymous so that i can respond to you through your name and don't make use of Names such as "Admin" or "ADMIN" if you want your Comment to be published.
Regards,
JavaByChetan
Back To Home